Looking for the definition of FET? Find out what is the full meaning of FET on Abbreviations.com! 'Field Effect Transistor' is one option - get in to view more @ The Web's largest and most authoritative acronyms and abbreviations resource. .FET has 3 regions i.e. Active, saturated and cutoff region. The FET acts as an amplifier in the active region while it acts as a switch in the saturated and cutoff regions. Since the input (gate) is reversed biased, the input impedance of FET is very high in the range of 100M ohm which is why there is no current flow at the gate terminal. A FET amplifier is an amplifier that uses one or more field-effect transistors (FETs). The most common type of FET amplifier is the MOSFET amplifier, which uses metal–oxide–semiconductor FETs (MOSFETs). The main advantage of a FET used for amplification is that it has very high input impedance and low output impedance.
In this article, we compare and contrast bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field effect transistors (FETs).
Though both are transistors and have 3 leads and achieve similar functions, they're fundamentally different in composition. Thus, there are several key differencesbetween the 2 transistors.
The table below pinpoints many of the differences between BJTs and FETs.
| BJTsvs FETs | ||
| How it operates | BJTs | FETs |
| BJTsare current-controlled. They require a biasing current to the baseterminal for operation. | FETsare voltage-controlled. They only require voltage applied to the gateto turn the FET either on or off. They do not require a biasing currentfor operation. | |
| InputImpedance | BJTsoffer smaller input impedances, meaning they draw more current from thepower circuit feeding it, which can cause loading of the circuit. | FETsoffer greater input impedance than BJTs. This means that theypractically draw no current and therefore do not load down the power circuitthat's feeding it. |
| Gain (Transconductance) | BJTsoffer greater gain at the output than FETs. | Thegain (or transconductance) of FETs are smaller than for BJTs. |
| Size | BJTsare larger in size and therefore take up more physical space than FETs normally. | FETscan be manufactured much smaller than BJTs. This is especiallyimportant for integrated circuits that are composed up of manytransistors. |
| Popularity | BJTsare lesspopular and less widely used | FETSare definitely more popular and widely used in commercial circuitstoday than BJTs |
| Cost | BJTsare cheaperto manufacture | FETs,especially MOSFETs, are more expensive to manufacture |
So the above table is a good, brief explanation of some of the differences between bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field effect transistors (FETs). Below we'll go over the table in more depth, so that you can get a better in-detailed explanation, if you feel the above lacked. We'll go in order.
So the first thing is how both transistors operate. BJTs are current-controlled devices. This means that BJTs are switched on by a current going through the base of the transistor. This base current then turns the BJT on, allowing for a much greater flow of current from the collector to the emitter of the transistor. FETs, on the other hand, are voltage-controlled. Voltage, not current, either turns the FET on or off. FETs have such high input impedance that they practically draw no current into the gate terminal. Instead they are entirely voltage-controlled.
The second difference is the input impedance. Input impedance is the amount of resistance that a transistor offers on its input terminal. For BJTs, this would be the base terminal; for FETs, this would be the gate terminal. BJTs offer much less resistance to their input terminal than FETs. Because of this much lower resistance, it draws current from the power supply powering the base. This is an effect called loading. Loading is when the power source circuit is affected by a second circuit, in this case the transistor circuit, which is drawing current from it. This small amount of currentdrawn, which then combines with the much larger current flowing from the other 2 leads can alter dynamics of the power source circuit. So BJTs offer less protection against this loading effect than FETs. FETs have very large input impedances, such as on the order of 1014 Ω, which is several teraohms (something you almost never hear about). With such high input impedance, the FETpractically draws no current to its input gate terminal. Therefore, since practically no current is drawn from the power supply circuit, the power supply circuit is not loaded down. It's as if the power supply circuit and the transistor circuit are well isolated and do not interfere with each other. Therefore, better power control is achieved with FETs with less interference of one circuit onto another.
A third difference between BJTs and FETs is the gain (or transconductance). Transconductance is defined as the milliamp per volt ratio of the small change in the current output from an electronic device to the small change of voltage input. In other words, it is the gain of the transistor circuit. This is where BJTs have an advantage. BJTs have greater transconductance, meaning you are able to get more current output per unit power applied. The transconductance of FETs is much lower. So if you use the same amount of power at the input for both a BJT and FET transistor, the BJTtransistor will produce more gain. This is why BJTs are more popular for amplifier circuits. They produce gain than a FET can. This is why in the case of simple amplifier circuits, the use of a BJT is preferred and FETs are rarely used. For simple amplifiers, FETs are really only used only when it is desired for there to be extremely high input impedance.

In terms of manufacturing size, FETs can be manufactured to be much smaller than BJTs. This makes them moreefficient in commercial circuit design. Being that FETs are smaller, they take up less space on a chip. Thus, the sizeof a electronic product can be much smaller, which is what electronic design companies want a lot of times. Smaller devices, many times, can be more convenient, consumer-friendly, and FETs allow this. BJTs, on the other hand, require larger sizes generally than FETs.

In terms of expense, FETs, especially MOFSFETs, are more expensive to manufacture than BJTs. FETs normally are at a higher price point, but not significant enough to push away from them. This is just a slight drawback.
For a number of reasons, such as those listed above, FETs are more widely used and more popular than BJTs. FETs can be manufactured smaller and load the power supply less.
So while BJTs are used widely in hobby electronics and many times too in some consumer electronics and have the advantage of being able to produce higher gains than FETS, FETs still offer many advantages for large-scale commercial devices. When it comes to consumer products, FETs areoverwhelmingly preferred due tosize, high input impedance, as well as other factors. Intel, one of the largest chip makers in the world, uses practically only FET transistors to build its chips which power billions of devices in the world.
Thus, this is a brief overview of FETs vs BJTs.
Related Resources
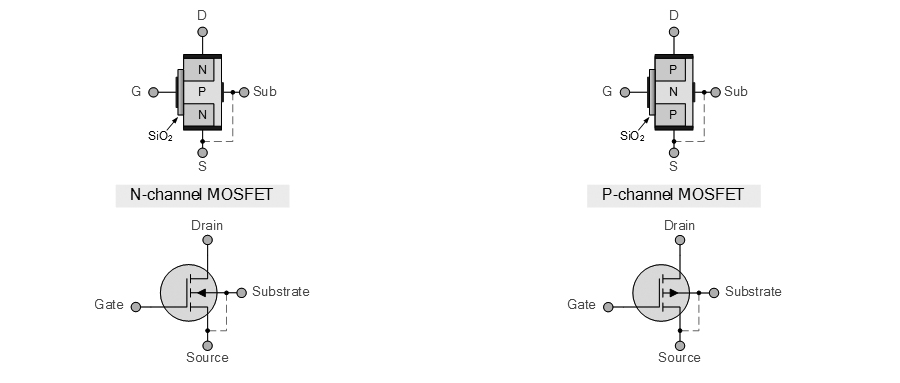
JFET vs MOSFET (Transistors)
Types of Transistors
Difference between an NPN and a PNP Transistor
Transistor Schematic Symbols
How is FET a voltage controlled device?
the voltage applied between the gate and the source controls the drain current (id). which means you use the voltage to control the output current. therefore, fet is a voltage controlled device.
just explained because it consumes very little power to operate. it relies on the voltage differential to create a field effect necessary for its operation (hence the field effect transistor name). the amplitude of the voltage differential dictates the operating speed of the device.
A FET is voltage controlled device by virtue of the fact that current flow between the Drain and the Source is controlled by the voltage at the Gate in reference to the Source (Vgs).
a fet is controlled by a voltage at the terminal of the gate and, because of the very high grid impedance, flows in or out of the gate. compare to a bipolar transistor in the active state which is controlled by the current flowing from the base to the emitter, which allows to obtain a collector-emitter current proportional to the base-emitter current.
a fet is a voltage-controlled device because the current between the drain and the source is controlled by the voltage at the gate with reference to the source (vgs).
This contrasts with the current controlled bjt because the current flow between the collector and the emitter is controlled by the current flowing through the base.
why is a FET voltage controlled device?
The most common type of fet is a type of insulated door. since the door is isolated from the drain and the source, no current can cross it (or very little, in practice). the fet has no choice: it can not be controlled by the current, it must be controlled by the electrostatic field created by the voltage on its grid. (hence its name: field effect transistor.)

or something like that!
To be short and simple:
You vary the voltage at the terminal, you get a constant current at the output. this is because the gate voltage is used to control channel resistance or pinch condition.
While a transistor is a current-controlled device because the base current is used to control the output collector current (taking into account the configuration of the common emitter).
How Does Current Flow In A Fet
in practical cases, the mosfet is better than the fet (the effects of ionization in the fet make it unfit for use in practical circuits). that’s why we’ve installed a layer of metal oxide on the fet to improve its applications.

For more detailed explanations, study the output response graphs of fet and compare them with those of mosfet.
jfet is a voltage-controlled device because the input signal is applied to the reverse-biased pn junction (source gate), which allows only a leakage current (in nano amps). the input bias current is negligible, the voltage having a dominant effect (very high impedance of 100 megohms). the output current flows from the source to the drain; the variation of the gate voltage controls the drain current. Instrumentation amplifiers
Feet Is A Measurement Of
jfet are used to amplify thermocouple signals in the microvolt range since virtually no bias current is drawn from the sensor.
by comparing bjt, it uses a live-biased pn junction inrush current in a range from micro to milliamps, resulting in low input impedance. Here, the change of the base current controls the greatest variation of the current of the collector. therefore, bjt is a current controlled apparatus.
it can be noted that in the two amplifiers bjt jfet, the voltage signals are given as input.
Which device is a voltage controlled device?
